As CPUs become more powerful, their thermal loads increase, necessitating advanced cooling solutions. Acetone heat pipes have emerged as an effective method for managing high heat fluxes in processors due to their excellent thermal conductivity, low boiling point, and efficient phase-change properties.
We found that under extremely harsh conditions, the cold and thermal shock test caused the heat pipe to expand, which is due to the fact that the traditional heat pipe uses pure water.When the product is used vertically in a -55°C environment, the liquid water that collects at the bottom quickly freezes, causing the volume to expand, which in turn causes the heat pipe to expand. At the same time, we know that water freezes at zero degrees, and when it freezes the heat pipe loses its“activity", which leads to heat buildup and even burns out the chip!
In order to solve the above problems, Pioneer Thermal brings customers a low temperature resistant heat pipe heat sink design, which uses acetone instead of water as the heat pipe working fluid inside the heat sink heat pipe, effectively avoiding the icing of the work material in the very low ambient temperature, thus protecting the cooling system, modules and the overall design from damage.
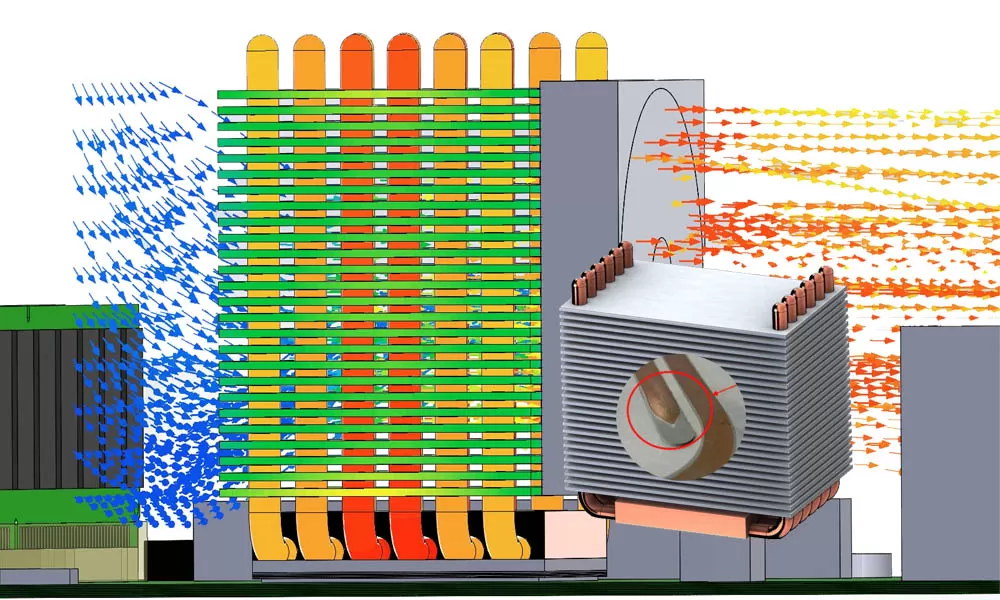
How Acetone Heat Pipes Work
Heat pipes are passive two-phase heat transfer devices that rely on the evaporation and condensation of a working fluid. When used for CPU cooling:
1. Evaporation Section (Hot Side – CPU Contact)
○ Heat from the CPU vaporizes acetone inside the heat pipe.
○ Acetone’s low boiling point (56°C) allows rapid vaporization, absorbing large amounts of heat.
2. Vapor Transport
○ The vapor moves to the cooler end (condenser section) due to pressure differences.
3. Condensation Section (Cooling Fins/Radiator)
○ The acetone vapor releases heat and condenses back into liquid.
○ Capillary action in the wick structure returns the liquid to the evaporation zone, completing the cycle.
Advantages of Acetone in CPU Heat Pipes
● High Heat Transfer Efficiency – Acetone’s latent heat of vaporization (538 kJ/kg at 25°C) allows efficient heat absorption.
● Low Boiling Point – Ideal for cooling modern CPUs that operate at 60–90°C.
● Lightweight & Non-Corrosive – Unlike water, acetone does not corrode copper or aluminum heat pipes.
● Fast Thermal Response – Acetone’s low viscosity ensures quick circulation, improving cooling under dynamic loads (e.g., gaming, rendering).
● Compatibility with Compact Designs – Suitable for laptop CPUs and small-form-factor PCs where space is limited.
Applications in CPU Cooling
● Desktop PCs & Workstations – Enhances cooling for high-TDP (Thermal Design Power) CPUs (e.g., Intel Core i9, AMD Ryzen 9).
● Gaming Laptops – Reduces throttling by efficiently dissipating heat in confined spaces.
● Overclocking Systems – Provides stable cooling under extreme thermal loads.
● Server & Data Center CPUs – Improves energy efficiency in high-density computing environments.
Future Developments
Hybrid Cooling Systems – Combining acetone heat pipes with liquid cooling or vapor chambers for extreme cooling.
Nanofluid Enhancements – Adding nanoparticles to acetone to improve thermal conductivity.
Advanced Wick Structures – Optimizing sintered metal or graphene wicks for faster fluid return.
Acetone heat pipes offer a highly efficient, lightweight, and responsive cooling solution for modern CPUs, particularly in high-performance and compact systems. While challenges like flammability and pressure management exist, ongoing research in materials and design continues to enhance their viability. As CPU power demands grow, acetone-based heat pipes could play a crucial role in next-generation thermal management.
- Acetone Heat Pipes
Tags :


 +86-18902844286
+86-18902844286
 E-mail
E-mail
